The nano-structured silica grade of toothpaste (ZEO6)
The nano-structured silica grade (ZEO6) shows a great application in oral care product. It can use in manufacturing of toothpaste, tooth powder and gel, as it helps in removing plaque and stain as well as whiten the teeth. This grade of silica function as thickening and cleaning agent and it acts as an abrasive to help to remove plaque and food particles from your teeth when brushing with toothpaste.
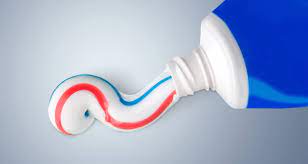
Precipitated silica is commonly used as an abrasive agent in toothpaste due to its mild abrasive properties. It works by physically removing plaque, stains, and debris from the teeth’s surface.
When you brush your teeth with toothpaste containing precipitated silica, the small particles of silica act as a gentle scrubbing agent. As you brush, these particles help to mechanically remove plaque and surface stains from the teeth.
The abrasive action of precipitated silica is important for maintaining oral hygiene. It helps to remove food particles, bacteria, and other substances that can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease. Additionally, it can help polish the teeth, making them appear cleaner and brighter.
Precipitated silica is commonly used as a thickening agent in toothpaste due to its ability to increase the viscosity and stability of the product. It works by absorbing water and forming a gel-like structure, which helps to control the flow and consistency of the toothpaste.
When added to toothpaste formulations, precipitated silica particles disperse throughout the product, creating a network that traps water and other ingredients. This network gives toothpaste its desired texture and prevents it from separating or becoming too runny.
Overall, precipitated silica as a thickener agent in toothpaste contributes to its desirable texture, stability, and cleaning effectiveness.

Precipitated silica and fumed silica are two different types of silica with distinct properties and manufacturing processes.
Energy Requirement:
Precipitated Silica: The manufacturing process for precipitated silica involves mixing chemicals, precipitation, filtration, washing, drying, and milling. This process requires less energy compared to the production of fumed silica.
Fumed Silica:
The production of fumed silica involves high-temperature reactions in a flame reactor using silicon compounds. This process requires significant energy input due to the need for high temperatures.In summary, precipitated silica has larger particle sizes, lower surface area, and requires less energy during its manufacturing process compared to fumed silica. On the other hand, fumed silica has smaller particle sizes, higher surface area, and requires more energy for its production.
Manufacturing Process:
Precipitated Silica: It is produced by adding a mineral acid to a solution of sodium silicate, resulting in the precipitation of amorphous silica particles.
Fumed Silica: It is manufactured by burning silicon tetrachloride or silicon compounds in a flame of hydrogen and oxygen, leading to the formation of fine, nanoscale particles of amorphous silica.